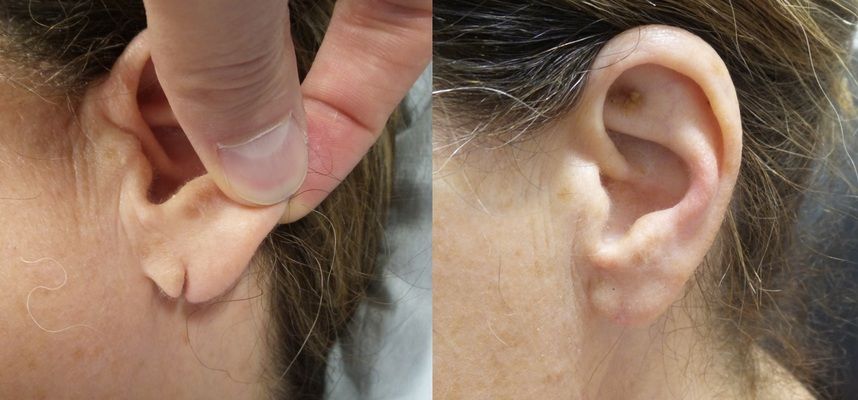
The earlobes are the parts of the ears made of skin and a small amount of fatty tissue. Earlobes often come in different sizes, shapes and thicknesses. They are also used to showcase jewelry in the case of both men and women. It is extremely common to get your ear lobes pierced to fit specific forms of earnings ranging from small diamond studs to more massive, extensive gauges. It is important to be careful with your choice in earrings; an overabundance of weight or trauma to the earlobe can cause a tear to occur. Something as simple as an earing being too heavy or a baby pulling on an earring could cause it to tear. Many find this split to be unattractive and uncomfortable and it of course negates the use of traditional earrings. Clip-on earrings can still be used and often are to hide the tear.
At Metro ENT Care your torn earlobes can be efficiently and safely corrected using delicate surgical techniques. It is important to speak with our doctor in order to figure out which procedure is best for you. The process is performed in our office under local anesthesia with other optional sedatives. The procedure is performed without any discomfort.
Our average procedure begins with removing the previously healed and scarred area of the earlobe in order to correct it. We then repair the tear using the technique we would have previously discussed with the patient. It is important to make sure an infection does not occur in the repaired area in the days following the procedure. Antibiotic ointment would then need to be applied at home for several days to ensure cleanliness. Once the earlobe has healed, you would barely see a pencil-fine scar line without aesthetic limitations.
The earlobe can be pierced again, however, we do insist that our patients wait a minimum of 8 weeks before re-piercing their lobes in order to minimize the risk of complications. It is essential to prevent repeated earlobe damage. Make sure to wear light earrings and to avoid wearing easily grabbed earrings around small children.
Please note, this procedure is not covered by insurance.*